

Energy
What GB’s Battery Energy Storage Market Means for the Planet
Many of the products and devices that we use every day have a huge impact on the planet. We often don’t think much about the environmental consequences, but they can be substantial if you don’t keep them in check.
Batteries are among the devices that have a huge, negative effect on the planet. A growing number of people are starting to reconsider the amount of batteries that they use for their various products. Friends of the Earth talks about some of the problems that batteries are creating. As the annual energy production of the lithium ion industry is expected to grow from 100 gigawatt hours (GWh) to nearly 800 GWhs by 2027, fears about the problems will continue to rise.
Great Britain is home to a rapidly growing battery market. It is important to understand the state of the battery market in this country and the effects that it will have on the planet.
What is the State of the Battery Market in the UK and How Does it Harm the Planet?
We will discuss the likely environmental impact of the UK battery market. However, it is first important to put it in context by understanding its size.
World-class battery research professionals and reputable businesses are already based in the United Kingdom. It’s also an exciting moment for Great Britain to store battery power after Brexit, as per the esteemed Faraday Institute.
The country is in good condition to take the lead in developing lithium-sulfur, salt ion, and other types of advanced batteries. For some years, Great Britain has earned international recognition as a low-carbon industry destination. In 2021, GB ranked 4th on the EY Renewable Country Attractiveness Index, after France and Germany.
But let’s talk about everything in more detail.
Review of the market
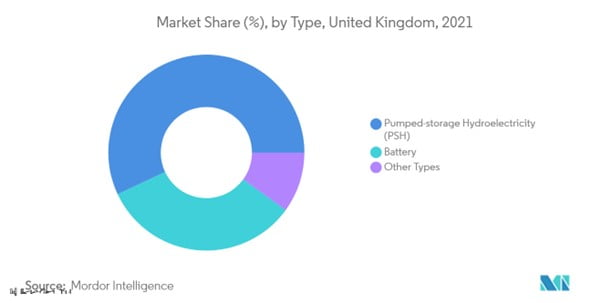
The industry of energy storage systems (ESS) in Great Britain is estimated to grow by over 21.34% CAGR at the end of 2022, totaling 292.3 MW.
Pandemia had an unfavorable impact on the industry in 2020. At this point, the sector had returned to pre-pandemic rates.
- Long-term market growth is anticipated to be fueled by the expanding field of the sustainable power sector, government laws, and support programs for ESS, and raised the economics of energy storage (ES).
- As opposed to that, starting in the spring of 2019, the closure of FiT and other aid strategies in the nation has made it more difficult to adopt rooftop solar systems, which might harm the market’s expansion and is one of its primary challenges.
- During the projected time frame, growth possibilities are anticipated as ESS use increases in the business and industrial segments.
General Trends
Battery ESS is predicted to be quite popular. Many of the environmental concerns about batteries are valid, but there are also clear benefits. For example, new batteries are helping store energy made with renewable power. New generations of rechargeable batteries are also better for the planet.
Evolving toward a sustainable energy system, batteries are viewed as a necessary technology. Battery energy storage (BS) options are used for additional power sources, peak usage reduction, renewable energy (RE) integration, voltage, and frequency management. ESS depends heavily on batteries, which also charge about 60% of the service’s overall cost.
Due to their falling costs, lithium-ion batteries have recently been in extremely high need in the UK’s ESS sector. Li-ion batteries are furthermore anticipated to have the biggest market share for battery ES due to their low maintenance requirements, lightweight, extended cycle durations, the high energy density per volume, and favorable charge/discharge effectiveness.
As per Renewable UK, the number of projects regarding ES in the UK has risen from an estimated 1,059 in 2021. A storage capacity of over 20 GW will be available for general BS by 2021, and 800 projects will be functional in the process of building or undertaking in the United Kingdom. To facilitate the incorporation of more low-carbon energy, heat, and transportation, adaptable technology such as batteries are thus likely to become a component of the UK’s enhanced grid. This is estimated to preserve the industry in Great Britain by growing up to $60 billion by 2050.
Some of these advances in battery storage are driving the future of sustainability. For example, Sembcorp intended to complete the largest ESS business initiative for lithium-ion batteries in the UK in December 2021. It’s expected that Wilton International in Teesside will host the construction. The project’s first stage will be finished by Sembcorp by 2023, while the remaining portions will be completed over time. 360 MW of storage will likely be available at one location once finished, where Sembcorp has free land and infrastructure prepared for battery construction. Thus, during the programmed period, such forthcoming initiatives will probably result in a rise in the UK Kingdom’s necessity for batteries.
As a result, in May 2021, RES stated that it had obtained approval to create a 99.9 MW storage plant that is scheduled to be operating by the end of 2023. The campaign, a lakeside power storage facility, is situated in North Yorkshire’s Selby neighborhood. Within the utility battery initiative, power from the electricity network will most definitely be stored during periods of little demand and lots of RE output and supplied back to the system during periods of high demand and little RE sources production. Thus, during the predicted timeframe, such forthcoming initiatives will probably result in a rise in the consumption of batteries in Great Britain.
Therefore, it is anticipated that demand for battery ESS will increase throughout the projected period due to future ES programs in the nation and the requirement to incorporate RE sources into the electric grid.
The need for ES devices will increase as the sector of renewable energies expands.
The requirement for ES for use in periods of peak demand arises from the intermittent and variable production of electricity from renewable resources like wind and sunlight.
As a result, cutting-edge ESS are increasingly being included in sustainable energy initiatives. One of the fastest-growing factors for the ESS industry in the UK is probably the quickest-growing RE segment.
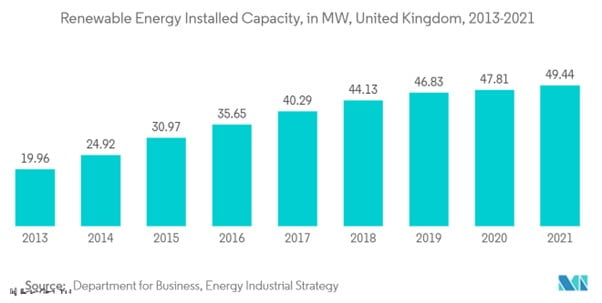
With an accumulated RE generation of around 49.44 GW in 2021, RE capacity has lately increased significantly. In 2021, RE sources produced more than 42% of the nation’s primary power requirements, a 129% increase over 2013’s 53.21 TWh total.
Beneficial government regulations, lower costs for wind and solar power equipment, and agreements to lessen a nation’s expanding carbon footprint are a few of the key elements promoting capacity increase.
The British government decided against raising corporate rates in November 2021 for solar PV, energy storage, and other RE technologies. The regulation will become operative in April 2023. The campaign will encourage firms to increase the usage of RE because of the reduced investment needs. Rooftop photovoltaic solar panels and combined usage of batteries and RE sources are examples of technologies covered under the law. For the past five years, the biggest businesses in the nation have been working to bring about these reforms.
In May 2022, ABB and Ecotricity announced their collaboration to construct a 10 MW center for storing batteries at the 6.9 MW Ecotricity wind farm in Gloucestershire in 2023. A 10MW/20MWh lithium-ion system for ES will be used in the project. The lithium-ion batteries will be provided by KORE Power, while ABB’s Storage OS system for energy management will control BESS.
Thus, the sustainable power industry is anticipated to have considerable expansion throughout the projection period thanks to support from the government, energy protection implications, and cost reduction, which will raise the need for ES technologies.
The Growing Battery Market Has Unclear Environmental Impacts in the UK
What’s the secret behind the UK’s rise in energy storage? A rebound in green investment has been made possible by recent political promises made by the country’s authorities.
The UK’s Energy Security Policy 2022, which is based on the state’s “clean zero strategy,” is foremost among them. This is intended to attract £100 billion in private funding. This made the environment more suited for ES.
The longer-term objective is to foster an environment for green energy investment in which ES plays a significant role in developing the country’s infrastructure.


 Environment12 months ago
Environment12 months agoAre Polymer Banknotes: an Eco-Friendly Trend or a Groundswell?

 Features11 months ago
Features11 months agoEco-Friendly Cryptocurrencies: Sustainable Investment Choices

 Features12 months ago
Features12 months agoEco-Friendly Crypto Traders Must Find the Right Exchange

 Energy11 months ago
Energy11 months agoThe Growing Role of Solar Panels in Ireland’s Energy Future


























