

Energy
Should You Use Solar or a Generator as an Eco-Friendly Homesteader?
When you decide to leave an eco-friendlier lifestyle, you might want to create your own homestead. This may entail creating a new property that doesn’t rely extensively on traditional electricity.
There are a lot of things that you need to do when you want to become an eco-friendly homesteader. You have to think about how you will power your property. There are a variety of options that are better for the environment than turning to the electric grid, but you have to weigh all of the pros and cons.
Considering Your Energy Options as an Eco-Friendly Homesteader
As soon as you get away from the comfort and convenience of your home or business, you’ll likely miss things. And no matter what that getaway is about, the first thing you’ll miss is surely going to be power. The same applies to the ever-present possibility of power outages.
Whether you are camping, working on an isolated job site, or welding a gate-hinge in a back pasture you’ll need power. And, out in the boondocks, that doesn’t really leave you with many options. Essentially you either go battery backup with solar energy or fire up the trusty gas generator. Either way, problem solved, right?
Well, yes and no. Both will get the job done for sure, but both have significant pros and cons which raise one important question. Which is better for my primary or backup power situation, solar battery backup power or a generator.
Solar vs generators: The pros and cons
Having a ready source of DC or AC power is an essential component of camping, power outage situations, or working in remote locations. And each one of these scenarios presents different requirements regarding the source of those power supplies. Firstly, let’s look at the specifics and pros and cons of installed solar power systems with battery storage, solar generators, and solar generators.
Installed solar systems
In the context of this article, an installed solar system is any solar setup in a residential home, an RV, camper van, or boat. In other words, one permanently mounted on the vehicle or in the home irrespective of the backup power system chosen.
Pros
- Quiet
- No emissions
- No hazardous fuel storage issues
- Efficient and effective weather permitting
- No additional running costs
- Low maintenance costs
- Solar panel arrays are part of the package
Cons
- Only as effective as the weather allows it to be.
- Limited to the vehicle or home and the area around immediately around it.
- Generally expensive to install
Solar generators
The specifics
Solar generators are essentially mobile versions of the installed solar systems detailed above. Entirely self-contained, they feature solar panels, charge controllers, batteries and battery maintainers, and inverters.
Pros
- Quiet
- No emissions
- Fully mobile
- No hazardous fuel storage issues
- Efficient and effective
- No additional running costs
- Low maintenance costs
Cons
- Only as effective as the weather allows it to be.
- Limited capacity due to space constraints
- Requires a separate solar panel
Gas, diesel, or propane generators
The backup generator has been around forever and with modern technology, is more efficient and effective than ever before. Whether they’re powered by gasoline, diesel, or natural gas, here are their pros and cons.
Pros
- Not affected by weather conditions
- Mobile
- Predictably powerful
- Reliable
Cons
- Noisy
- Requires storage and transport of hazardous natural gas, fuel and oil
- Higher running costs
- Higher maintenance costs
So, where do these remote power sources shine or fade?
All off-grid situations require one common resource. A reliable, sustainable power source. Obviously, the pros and cons of each relevant power source option create overlapping grey areas and a lot of potential for collaboration.
The following comparisons have been based on two scenarios. The first is a single choice situation where users would have to choose between a solar system or a generator. The second scenario allows users to choose between a solar system, generators, or a combination of the two. The choices are then broken down into primary, backup, and ideal power source option scenarios.
Home use
In these environments, power availability is marginally less critical in terms of financial and life support aspects. It tends to be more relevant to power outages and more comfort-centric. Users would typically choose a quiet, reliable primary solar option with gasoline or natural gas backup generators. This would make the ideal scenario a combination of both.
Recreational use
This area of remote power use is essentially identical to home use with an increased focus on comfort. Consequently, the choices would be the same, namely a primary solar system with a backup generator.
Business use
For the average contractor or business owner, generators are king. Mainly because noise is of little consequence and generator fuel and maintenance costs are built into their quotes. That said most would opt to have solar backup generators in case of a gas generator power failure. Again, the combination of a generator and a battery backup system is ideal.
Utility use
Here reliability is paramount and the generator reigns supreme. Even so, the job could potentially be dozens of miles from the nearest point of repair or re-equip. In the event of a generator power failure, a fully charged solar generator battery backup could prevent a time-consuming trek back home. And thus, the combination choice is once again the ideal.
Emergency and disaster relief use
Here we are dealing with life-threatening situations where intervention can literally mean the difference between life and death.
I know for a fact, were I the head of a search and rescue team, I would rely exclusively on powered generators. Partially because an extended fuel supply would not be an issue but reliability under all conditions would certainly be.
Even so, if I was a SAR head, I would definitely include a large-capacity solar generator in my inventory as a backup.
A visual representation
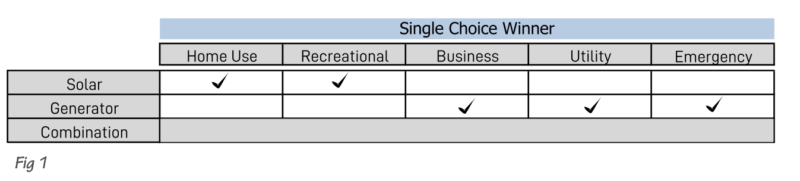
Here are the basic takeaways in table form starting with a single choice winner selection.
Now for the multiple-choice results.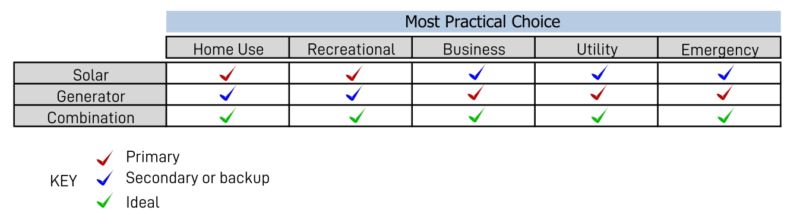
Single choice winners
To clarify, users in the home and recreational categories would typically choose to use solar. Mainly because of the low operating costs and lack of intrusive noise and emissions.
Users in the business, utility, and particularly the emergency fields would opt for a generator. Primarily because they’re more reliable in any given set of weather conditions and the reduced latency of fuel costs and storage.
Multiple choice winners
However, they would all choose to have either a gas generator or a solar generator in reserve as an ideal scenario if space and budget allowed it.
Consider the Merits of Generators and Solar as an Eco-Friendly Homesteader
The solar vs gas generator debate is not new with each side of the fence populated by enthusiastic supporters in the eco-friendly homesteading community. Despite that, if you are impartial in your approach to that debate, it becomes clear that each carries equal merit.
And, in fact, they complement each other more than they compete for popularity or market share. Where one falls down, the other shoulders the load, and a combination of both will usually be the better choice.


 Environment12 months ago
Environment12 months agoAre Polymer Banknotes: an Eco-Friendly Trend or a Groundswell?

 Features11 months ago
Features11 months agoEco-Friendly Cryptocurrencies: Sustainable Investment Choices

 Features12 months ago
Features12 months agoEco-Friendly Crypto Traders Must Find the Right Exchange

 Energy11 months ago
Energy11 months agoThe Growing Role of Solar Panels in Ireland’s Energy Future


























