Environment
10 Tips for a Successful Biological Pest Control Program
With the growing concern for the environment, more consumers are turning to eco-friendly pest control products that minimize the risk of harm to the ecosystem, pets, and humans. The market for environmentally friendly pest control was valued at $4.96 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow to $8.83 billion by 2030, reflecting a growing hunger for sustainable solutions. Many people are actively attempting to align their daily choices with environmentally friendly values, including how they manage pests in and around their homes and gardens.
This is also tied into overall lifestyle trends. An article in Forbes recently discovered that 77 percent of people surveyed would prefer to know how to live more sustainably, showing that interest in greener lifestyles in general is high. In addition, Caitlyn Fallon of the National Wildlife Federation says that one out of three (or 34 percent of) U.S. adults now buy plants with the specific goal of providing for local wildlife, and they certainly don’t want to employ pest control methods that would undermine that objective.
“A survey commissioned by the National Wildlife Federation, in partnership with the National Gardening Association, found more people are gardening for wildlife by purchasing native plants and landscaping that help pollinators like at-risk butterflies, bees and birds. The survey is part of an annual consumer gardening report that coincides with the National Wildlife Federation’s 10th annual Garden for Wildlife™ Month,” Fallon writes.
As a result, earth-friendly pest solutions aren’t specialty anymore—they’re the new norm for the ecologically minded home.
What is biological pest control? The practice of biological pest control requires a deep understanding that enables successful program implementation, enhances crop health, and maintains beneficial species while protecting the environment. The following ten essential methods represent guidelines for achievement.
Understand Your Pest and Natural Enemies
Before beginning biological pest management, the first requirement is to detect the target pest and identify its potential natural enemies, parasitoids, and pathogens. Investigators should investigate all life stages of the pests to determine their behavior and how they interact with other organisms in their natural habitat. Partnering proper knowledge enables one to select effective control measures.
Choose the Right Biological Control Agents
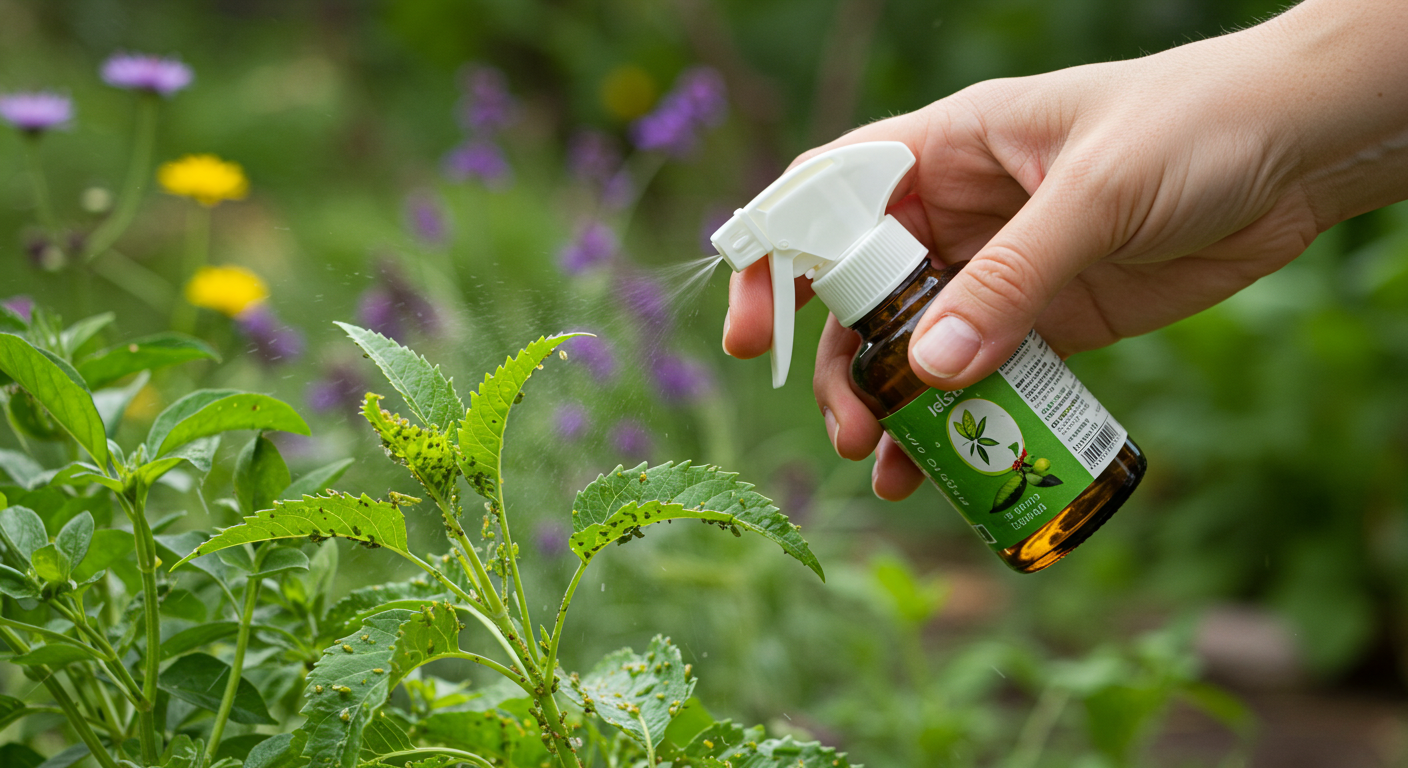
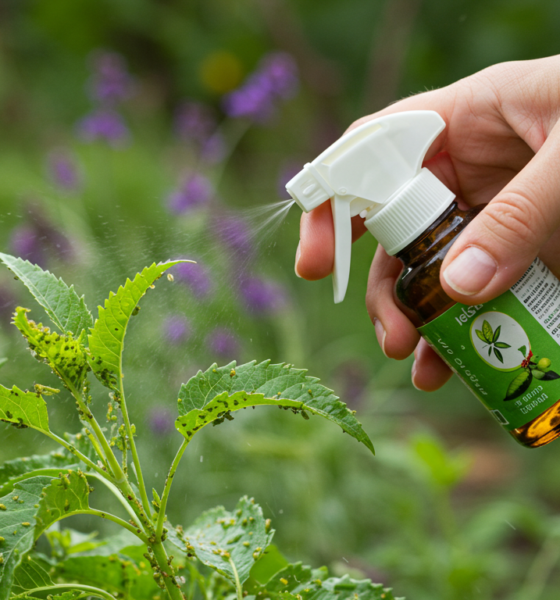
The management of various pests requires particular biological control agents. Ladybugs are predatory insects that specifically target aphids, whereas parasitoid wasps control the lifecycle of caterpillars. The microbial agent Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) is a practical solution against insect pests in their larval stage. Select the control agents that target pests attacking your crops. Businesses need to acquire biological control agents, specifically from trustworthy suppliers, to keep their functional properties intact and stop unwanted species from entering their operations.
Create a Supportive Environment
A suitable habitat is necessary to support the natural enemies of pests. Combining flowering plants with pollinators and predators benefits and proper ground cover creation provides protection. Everlasting tilling practices should be avoided because they destroy populations of helpful insects.
Reduce Chemical Pesticide Use
Continuous exposures to chemical pesticides completely eradicate pests and their natural predator species. IPM strategies must be implemented to prefer biological pest control while using chemicals only in critical circumstances. Excessive pesticide application creates resistant pests, making future infestation control efforts increasingly challenging.
Implement Proper Release Strategies
The right timing and appropriate location selection are essential in biological control agent deployment. To control their breeding practices, let biological control agents enter the environment when pest populations exist sustainably. Correct distribution methods combined with proper timing make these controls work better.
Monitor Pest and Predator Populations
Implementing routine monitoring helps identify pest outbreaks at an early stage and evaluates how well biological controls function. It is vital to implement traps combined with field surveys and proper record-keeping systems to track population changes and make strategic adjustments. Farmer records help track observations, which let them improve their biological control strategies through practical experience built over time.
Integrate with Other Sustainable Practices
Biological pest control is most effective when combined with environmentally friendly agriculture methods. Crop rotation and intercropping, along with soil management practices, lead to ecological balance, thus decreasing intense pest infestations. Pest attacks become less threatening when plant organisms have strong resistance due to healthy soils maintained through compost and organic fertilizers.
Train Farmers and Farm Workers
Education and training systems enable the correct usage of biological control methods. Farmer success will require proper identification of beneficial species, correct control agent application, and sustainable farming practices. Workshops, field demonstrations, and extension services enhance biological pest control knowledge and skills.
Stay Updated on New Innovations
Biological pest control remains an active scientific field where researchers follow constant developments and make progressively advanced discoveries. Continually update yourself about emerging biopesticides, genetic advancements, and innovative techniques because they will strengthen your pest management system.
Evaluate and Adjust Your Program
Accomplishment requires ongoing assessment merged with adaptive measures. Regular analysis of your biological control program should lead to needed adjustments based on monitoring pest populations, environmental shifts, and emerging scientific data. Working with agricultural experts and researching with researchers allows for better pest control methods.
Conclusion
An adequately maintained biological pest control system builds agricultural systems that resist environmental changes and simultaneously eliminate dependence on chemical pesticides while supporting native species. Thus, farmers who apply these ten guidelines can strengthen sustainability while retaining successful pest management approaches for continuous agricultural outcomes.


 Environment11 months ago
Environment11 months agoAre Polymer Banknotes: an Eco-Friendly Trend or a Groundswell?

 Environment12 months ago
Environment12 months agoEco-Friendly Home Improvements: Top 7 Upgrades for 2025

 Features10 months ago
Features10 months agoEco-Friendly Cryptocurrencies: Sustainable Investment Choices

 Features11 months ago
Features11 months agoEco-Friendly Crypto Traders Must Find the Right Exchange